Riesgo y resiliencia: una revisión de los rasgos funcionales que influyen en la vulnerabilidad al fuego en mamíferos del Pantanal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37002/biodiversidadebrasileira.v14i4.2565Palabras clave:
Ecología del fuego, Manejo de incendios, Vulnerabilidad al fuego, Fauna, Atributos funcionales, Incendios forestales, PantanalResumen
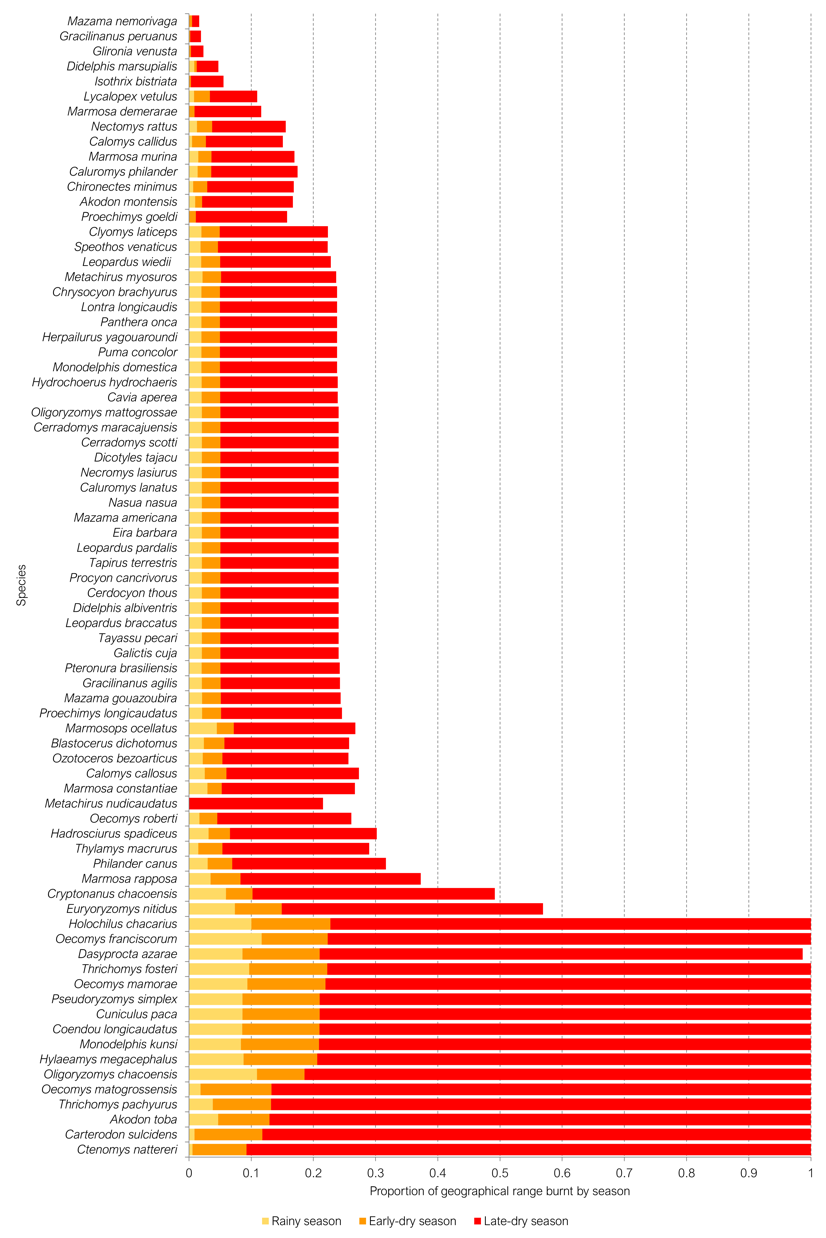
En 2020, el Pantanal brasileño experimentó incendios forestales sin precedentes que quemaron aproximadamente 40.000 km² y provocaron la muerte de por lo menos 17 millones de vertebrados. Este evento catastrófico, caracterizado por un comportamiento extremo del fuego facilitado por una combinación de materia orgánica acumulada en áreas inundadas de larga duración, comunidades de macrófitos, alfombras flotantes, pastizales abiertos y una sequía prolongada, ha destacado tanto la severa vulnerabilidad del ecosistema del Pantanal a los incendios forestales sazonales, como la necesidad de una comprensión integral de sus efectos potenciales sobre las especies y la dinámica del ecosistema. Este estudio explora la vulnerabilidad de los mamíferos a los incendios forestales en el Pantanal, centrándose en el análisis de los rasgos de vulnerabilidad al fuego y la distribución espacial de las especies. Revisamos un total de 2.868 estudios publicados desde 1938, que abarcan cinco órdenes de mamíferos: Artiodactyla, Carnivora, Didelphimorphia, Rodentia y Perissodactyla. El análisis reveló un aumento significativo en la investigación sobre los rasgos de vulnerabilidad al fuego, particularmente en carnívoros, desde el año 2000. Los rasgos más estudiados incluyen la preferencia de hábitat, el tamaño corporal y la dieta, mientras que otros rasgos críticos para comprender la sensibilidad al fuego recibieron menos atención. Nuestros descubrimientos destacan una sazonalidad acentuada en los regímenes de incendios y la especialización del hábitat entre las especies de mamíferos del Pantanal, con una superposición preocupante entre los incendios forestales de 2019-2020 y la distribución de varias especies, lo que sugiere posibles disminuciones severas en la abundancia y distribución. Los descubrimientos abogan por esfuerzos de conservación inmediatos dirigidos a hábitats clave y enfoques refinados de manejo de incendios forestales para mitigar los impactos, particularmente en especies geográficamente restringidas. También requiere un enfoque de investigación más equilibrado en diferentes taxones y rasgos para comprender completamente los roles menos estudiados frente al aumento de la frecuencia e intensidad de los incendios en el bioma del Pantanal.
Descargas
Citas
Libonati R, DaCamara Carlos C, Peres Leonardo F, de Carvalho Lino A Sander, Garcia Leticia C. Rescue Brazil's burning Pantanal wetlands. Nature. 2020;588(7837):217-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03464-1
Tomas WM, Berlinck CN, Chiaravalloti RM, Faggioni GP, Strüssmann C, Libonati R, et al. Distance sampling surveys reveal 17 million vertebrates directly killed by the 2020's wildfires in the Pantanal, Brazil. Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 1;11(1). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-02844-5
Garcia LC, Szabo JK, de Oliveira Roque F, de Matos Martins Pereira A, Nunes da Cunha C, Damasceno-Júnior GA, et al. Record-breaking wildfires in the world's largest continuous tropical wetland: Integrative fire management is urgently needed for both biodiversity and humans. Vol. 293, Journal of Environmental Management. Academic Press; 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112870
Kotze DC. The effects of fire on wetland structure and functioning. Afr J Aquat Sci. 2013;38(3):237-47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2989/16085914.2013.828008
Marengo JA, Alves LM, Torres RR. Regional climate change scenarios in the Brazilian Pantanal watershed. Vol. 68, Climate Research. Inter-Research; 2016. p. 201-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/cr01324
Nimmo DG, Carthey AJR, Jolly CJ, Blumstein DT. Welcome to the Pyrocene: Animal survival in the age of megafire. Glob Chang Biol. 2021 Nov 1;27(22):5684-93. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15834
Pausas JG, Parr CL. Towards an understanding of the evolutionary role of fire in animals. Evol Ecol [Internet]. 2018;32(2-3):113-25. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10682-018-9927-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10682-018-9927-6
Jones GM, Goldberg JF, Wilcox TM, Buckley LB, Parr CL, Linck EB, et al. Fire-driven animal evolution in the Pyrocene. Vol. 38, Trends in Ecology and Evolution. Elsevier Ltd; 2023. p. 1072-84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2023.06.003
González TM, González-Trujillo JD, Muñoz A, Armenteras D. Effects of fire history on animal communities: a systematic review. Vol. 11, Ecological Processes. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH; 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00357-7
Santos JL, Hradsky BA, Keith DA, Rowe KC, Senior KL, Sitters H, et al. Beyond inappropriate fire regimes: A synthesis of fire-driven declines of threatened mammals in Australia. Vol. 15, Conservation Letters. John Wiley and Sons Inc; 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12905
Engstrom RT. First-order fire effects on animals: review and recommendations. Fire Ecology. 2010;6(1):115-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4996/fireecology.0601115
Santos F, Bailey JK, Schweitzer JA. The eco-evolutionary role of fire in shaping terrestrial ecosystems. Vol. 37, Functional Ecology. British Ecological Society; 2023. p. 2090-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.14387
Leahy L, Legge SM, Tuft K, Mcgregor HW, Barmuta LA, Jones ME, et al. Amplified predation after fire suppresses rodent populations in Australia's tropical savannas. Wildlife Research. 2015;42(8):705-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/WR15011
Pausas JG. Generalized fire response strategies in plants and animals. Oikos. 2019;128(2):147-53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.05907
Sheets AD, Chavez AS. Evolution of pelage luminance in squirrels (Sciuridae). Front Ecol Evol. 2020;8:249. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2020.00249
Bowman DMJS, Kolden CA, Abatzoglou JT, Johnston FH, van der Werf GR, Flannigan M. Vegetation fires in the Anthropocene. Vol. 1, Nature Reviews Earth and Environment. Springer Nature; 2020. p. 500-15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-0085-3
Jolly CJ, Dickman CR, Doherty TS, Eeden LM Van, Geary WL, Legge SM, et al. Animal mortality during fire. Glob Chang Biol. 2022;28(6):2053-65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.16044
Calhoun KL, Goldstein BR, Gaynor KM, McInturff A, Solorio L, Brashares JS. Mammalian resistance to megafire in western U.S. woodland savannas. Ecosphere. 2023 Jul 1;14(7). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.4613
Santos FLM, Nogueira J, Souza RAF De, Falleiro RM, Schmidt IB, Libonati R. Prescribed burning reduces large, high-intensity wildfires and emissions in the Brazilian savanna. Fire. 2021;4(3):56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fire4030056
Batista EKL, Figueira JEC, Solar RRC, de Azevedo CS, Beirão M V., Berlinck CN, et al. In Case of Fire, Escape or Die: A Trait-Based Approach for Identifying Animal Species Threatened by Fire. Vol. 6, Fire. MDPI; 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6060242
Mahony M, Gould J, Beranek CT, Callen A, Clulow J, Clulow S, et al. A trait-based analysis for predicting impact of wildfires on frogs. Australian Zoologist. 2022;42(2):326-51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7882/AZ.2022.021
Griffiths AD, Brook BW. Effect of fire on small mammals: a systematic review. Int J Wildland Fire. 2014;23(7):1034-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/WF14026
Chia EK, Bassett M, Leonard SWJ, Holland GJ, Ritchie EG, Clarke MF, et al. Effects of the fire regime on mammal occurrence after wildfire: Site effects vs landscape context in fire-prone forests. For Ecol Manage [Internet]. 2016;363:130-9. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.12.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.12.008
Garcês A, Pires I. The hell of wildfires: the impact on wildlife and its conservation and the role of the veterinarian. Conservation. 2023;3(1):96-108. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation3010009
Massman WJ, Frank JM, Mooney SJ. Advancing investigation and physical modeling of first-order fire effects on soils. Fire Ecology. 2010;6(1):36-54. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4996/fireecology.0601036
Naves-Alegre L, Morales-Reyes Z, Sánchez-Zapata JA, Sebastián-González E. Scavenger assemblages are structured by complex competition and facilitation processes among vultures. J Zool. 2022 Dec 1;318(4):260-71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.13016
Lira LA, Aguiar LMS, Silveira M, Frizzas MR. Vertebrate scavengers alter the chronology of carcass decay. Austral Ecol. 2020 Dec 1;45(8):1103-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aec.12939
Demo C, Cansi ER, Kosmann C, Pujol-Luz JR. Vultures and others scavenger vertebrates associated with man-sized pig carcasses: A perspective in Forensic Taphonomy. Zoologia. 2013 Oct;30(5):574-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-46702013000500010
Culhane K, Sollmann R, White AM, Tarbill GL, Cooper SD, Young HS. Small mammal responses to fire severity mediated by vegetation characteristics and species traits. Ecol Evol. 2022 May 1;12(5). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8918
Briani DC, Palma ART, Vieira EM, Henriques RPB. Post-ï¬re succession of small mammals in the Cerrado of Brasil. Biodiversity and Conservation2. 2004;13(5):1023-37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOC.0000014467.27138.0b
Henriques RPB, Briani DC, Palma ART, Vieira EM. A simple graphical model of small mammal succession after fire in the Brazilian cerrado. Mammalia. 2006;70(3-4):226-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/MAMM.2006.044
McGee JM. Small mammal populations in an unburned and early fire successional Sagebrush community. Journal of Range Management. 1982;35(2):177-80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/3898385
Gosper CR, Prober SM, Yates CJ. Estimating fire interval bounds using vital attributes: Implications of uncertainty and among-population variability. Ecological Applications. 2013;23(4):924-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1890/12-0621.1
Smith SK, Young VKH. Balancing on a limb: effects of gravidity on locomotion in arboreal, limbed vertebrates. Integr Comp Biol. 2021;61(2):573-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icab035
Fagan WF, Lewis MA, Auger-Méthé M, Avgar T, Benhamou S, Breed G, et al. Spatial memory and animal movement. Ecol Lett. 2013;16(10):1316-29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12165
Kreling SES, Gaynor KM, Mcinturff A, Calhoun KL, Brashares JS. Site fidelity and behavioral plasticity regulate an ungulate's response to extreme disturbance. Ecol Evol. 2021;11(22):15445-6364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8221
Switzer P V. Site fidelity in predictable and unpredictable habitats. Evol Ecol. 1993;7:533-55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01237820
Pocknee CA, Legge SM, McDonald J, Fisher DO. Modeling mammal response to fire based on species' traits. Conservation Biology. 2023;e14062. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.14062
Legge S, Murphy S, Heathcote J, Flaxman E, Augusteyn J, Crossman M. The short-term effects of an extensive and high-intensity fire on vertebrates in the tropical savannas of the central Kimberley, Northern Australia. Wildlife Research. 2008;35(1):33-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/WR07016
Marel A van der, López-Darias M, Waterman JM. Group-enhanced predator detection and quality of vigilance in a social ground squirrel. Anim Behav. 2019;151:43-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2019.02.017
Decety J, Norman GJ, Berntson GG, Cacioppo JT. A neurobehavioral evolutionary perspective on the mechanisms underlying empathy. Prog Neurobiol [Internet]. 2012;98(1):38-48. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.05.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.05.001
Morelli F, Benedetti Y, Díaz M, Grim T, Ibáñez-Álamo JD, Jokimäki J, et al. Contagious fear: escape behavior increases with flock size in European gregarious birds. Ecol Evol. 2019;9(10):6096-104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5193
Socias-martínez L, Kappeler PM. Catalyzing transitions to sociality: ecology builds on parental care. Front Ecol Evol. 2019;7:160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2019.00160
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Os autores mantêm os direitos autorais de seus artigos sem restrições, concedendo ao editor direitos de publicação não exclusivos.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Os artigos estão licenciados sob uma licença Creative Commons Atribuição-NãoComercial-SemDerivações 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). O acesso é livre e gratuito para download e leitura, ou seja, é permitido copiar e redistribuir o material em qualquer mídia ou formato.











